Describe Use of Hemolysis in Diagnostic Bacteriology
We searched PubMed for all published cases of C. Hemolysis is of three types alpha or partial beta or complete and gamma or no hemolysis.

Microbiology Hemolysis Blood Agar Youtube
Hektoen enteric agar HE which is selective for Gram-negative bacteria.

. Use of the diagnostic bacteriology laboratory. Interpretation of Hemolysis on Blood Agar Plates To read the hemolytic reaction on a blood agar plate the plate must be held up to a light source and observed with the light coming from behind transmitted light. Use of the diagnostic bacteriology laboratory.
Starting cultures in the field improves the turn around and can improve the accuracy of diagnosis of some diseases. Al-though described more than a century ago the Gram stain remains the most frequently used. A practical review for the clinician W J Steinbach A K Shetty EVective utilisation and understanding of the clinical bacteriology laboratory can greatly aid in the diagnosis of infectious diseases.
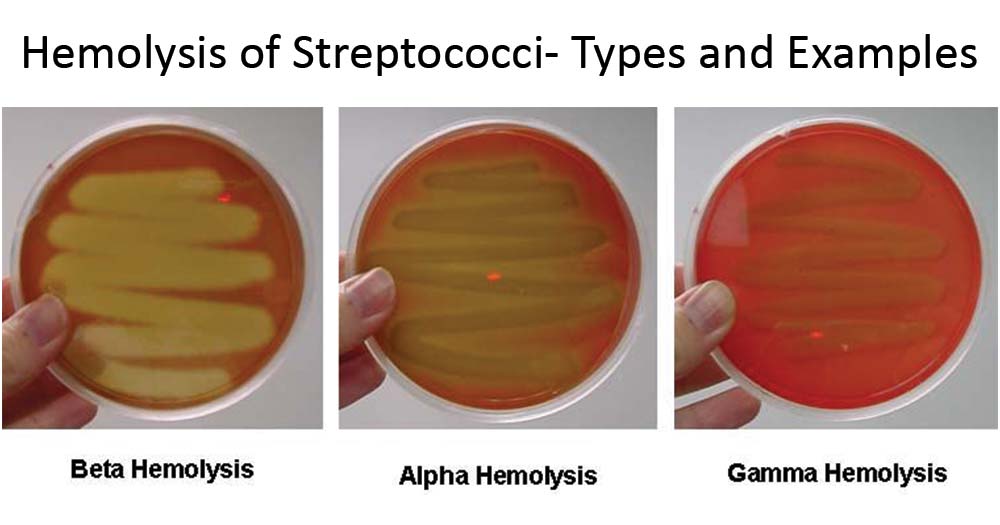
Beta-hemolysis β-hemolysis is associated with complete lysis of red cells surrounding the colony. Alpha-hemolytic streptococci are members of the normal throat flora and do not need to be identified further when they. Pneumoniae and viridans streptococci are alpha hemolytic Group A S.
Usually differentiate specific species by change in agar color. Hemolysis is also defined as erythrocyte necrosis and occurs at the end of every erythrocytes life. A substance that causes hemolysis is a hemolysin.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. It should be part of. Demonstrate the hemolytic activity.
Some bacteria are able to break down blood cells by a process called hemolysis. All these signs of hemolytic anemia fluctuated in parallel with. Specimen Collection Transport Processing.
Media that inhibit the growth of unwanted microorganisms and support the growth of the organism of interest by supplying nutrients and reducing competition are called selective mediaAn example of a selective medium is MacConkey agarIt contains bile salts and crystal violet which interfere with the growth of many gram-positive bacteria and favor the growth of. Agalactiae are beta hemolytic and Enterococci are gamma hemolytic Washington 19968. Beta hemolysis is the clear zone that surrounds the bacterial colonies in which the red blood cells have been lysed.
An enzyme produced by the bacteria which. YM yeast and mold which has a low pH deterring bacterial growth. We describe a case of hemolytic anemia with subacute bacterial endocarditis due to Streptococcus sanguis.
Microbiology - 010 - Hemolysis. Hemolytic anemia is defined by the premature destruction of red blood cells and can be chronic or life-threatening. I take aspirates using a 10-ml syringe and 15-inch 20-gauge needle.
Specialized agars selective and differential for various microbes. Alpha Hemolysis Beta Hemolysis Blood Agar Gamma Hemolysis hemolysis. On blood agar plates a small zone of alpha-hemolysis surrounded by zone of beta-hemolysis after refrigeration is known.
A specialized media that selects for the growth of organisms with particular characteristics. Eosin methylene blue EMB that contains methylene blue toxic to Gram-positive bacteria allowing only the growth of Gram negative bacteria. SI Units Plasma or serum will appear pink when the hemoglobin concentration exceeds 50 mgdL.
Brown 1919 introduced three terms alpha beta and gamma to indicate three types of streptococci based on haemolytic reactions observed on blood agar plates. After the necropsy spray the aspirate on blood agar plates. Describe the diagnostic criteria and clinical findings seen in RBC hemolysis Discuss the pathophysiology of AIHA Warm AIHA WAIHA Cold AIHA CAD CAS Assess current treatments for AIHA Review new approaches to treatment of AIHA.
Hemolysis is the breakdown of red blood cells RBC. Knowing what type of hemolysis a bacterial strain is capable of can be helpful in identifying several types of bacteria especially organisms isolated from human tissue such as Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species. The sample has to be processed and reported immediately.
The type of hemolytic reaction displayed on blood agar has long been used to classify the streptococci. Pyogenes and Group B S. The major hematological features of the patient were a normocytic anemia with reticulocytosis an elevation of serum lactate dehydrogenase and a marked reduction of serum haptoglobin.
MacConkey agar for Gram-negative bacteria. On blood agar plates a small zone of alpha-hemolysis surrounded by zone of beta-hemolysis after refrigeration is known. A good example of use of blood agar as a differential medium is seen in grouping Streptococci.
We describe the case of a patient with hemolysis-associated Clostridium perfringens septicemia and review all similar cases published in the literature since 1990 with specific focus on the relationship between treatment strategy and survival. This is an emergency procedure. In the clinical microbiology laboratory observation of hemolysis is an important first step in differentiating among streptococcal species.
Aureus or phenotypes like MRSA MSSA. Hemolysis is the disruption of erythrocyte membranes which causes the release of hemoglobin. Streptococcus spp and Enterococcus spp.
To reduce blood culture contamination rate collection may be improved by taking the following precautions. β-Hemolysis is associated with complete lysis of red cells surrounding the colony whereas α-hemolysis is a partial or greening hemolysis associated with reduction of. Bacteriology is not simple and safety precautions must be taken.
Beta hemolysis β is defined as. The hemolysis means breakdown of hemoglobin of the red blood cells. Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro.
Typical Normal Range US Units. This phenomenon is associated with some forms of Streptococcus that produce streptolysin. Collection and transport Purpose.

Hemolysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
No comments for "Describe Use of Hemolysis in Diagnostic Bacteriology"
Post a Comment